The Silent Ascendancy: Next-Gen Passive Cooling Tech
In the relentless pursuit of faster, more powerful electronics, one crucial aspect often gets overshadowed: cooling. The unsung hero of your laptop, smartphone, or gaming console, efficient cooling technologies safeguard the longevity and performance of your devices. Today, we delve into the fascinating realm of next-gen passive cooling technology—a sector quietly revolutionizing the electronics landscape.
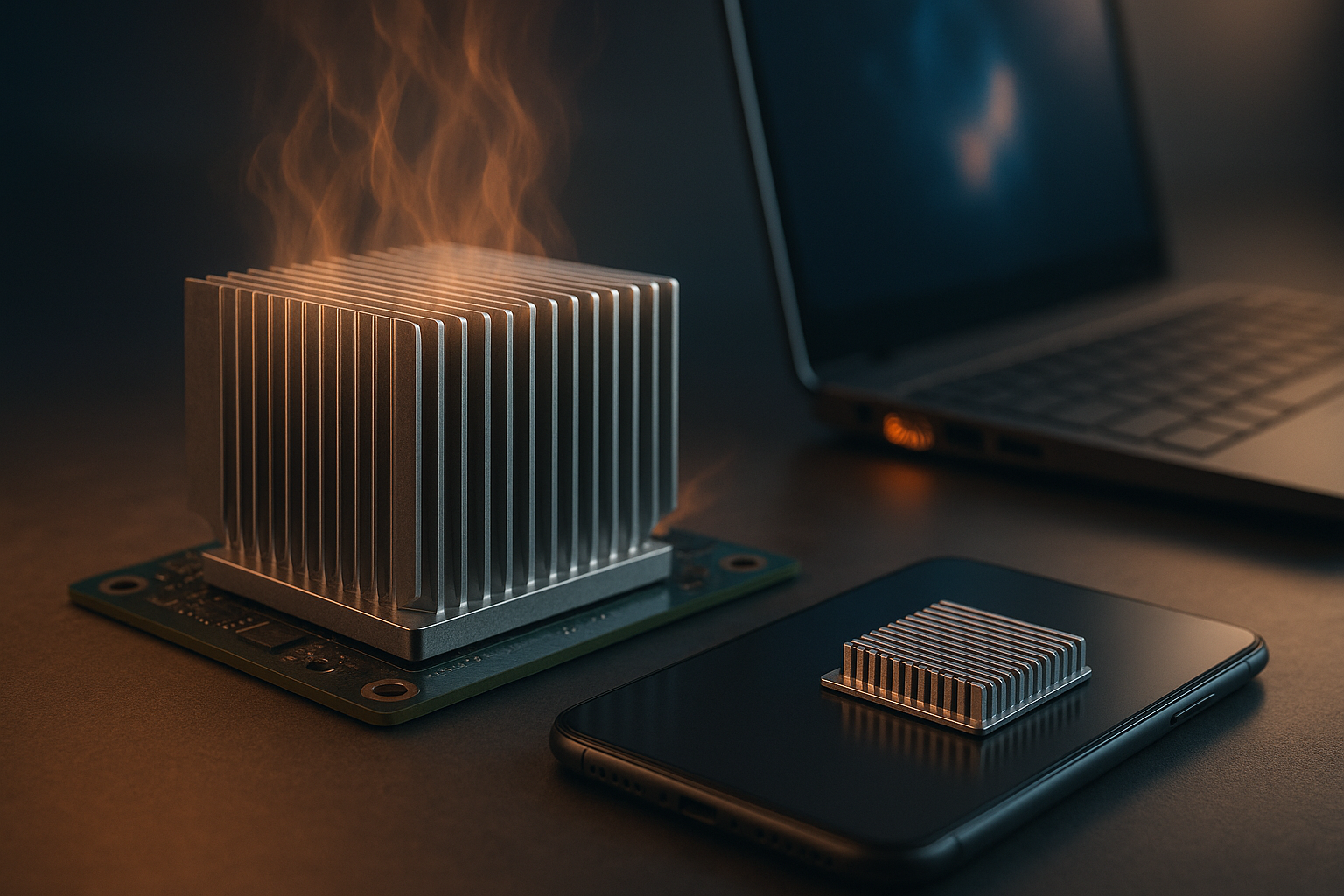

The Understated Importance of Cooling Tech
In the early days of computing, processors were modest and cooling demands minimal. However, as technology evolved and electronics became more powerful, the need for efficient cooling systems grew exponentially. The pivotal shift took place in the 1990s, when Intel introduced the Pentium chip—a processor so powerful, it necessitated an active cooling fan.
Fast forward to today, and cooling has become an essential feature of most electronics. From the humble laptop to the colossal data center, an effective cooling system ensures optimal performance and prevents thermal damage. Yet, amid the din of cutting-edge processors, high-resolution screens, and advanced battery tech, the importance of cooling often goes unnoticed.
The Rise of Passive Cooling
Active cooling systems, such as fans and liquid cooling, have been the dominant solution for decades. However, they have significant drawbacks, including noise, energy consumption, and potential mechanical failure. In contrast, passive cooling technologies offer a tantalizing alternative—quiet, energy-efficient, and devoid of moving parts.
The concept of passive cooling isn’t new. It has been around since the dawn of computing, primarily in the form of heat sinks—metal structures designed to dissipate heat. Yet, recent advancements are reinventing the game, yielding passive cooling solutions that are not only efficient but also incredibly thin, perfectly suited for today’s ultra-slim electronics.
The Vanguard of Passive Cooling: IceGiant and Sandia Cooler
Two companies, in particular, are leading the charge in next-gen passive cooling—IceGiant and Sandia National Laboratories. IceGiant’s ProSiphon technology, for instance, harnesses the power of gravity to circulate coolant, eliminating the need for pumps or fans.
Meanwhile, Sandia National Laboratories has developed the Sandia Cooler—a heat sink that doubles as a fan. Its patented design reduces energy consumption by 30% and achieves ten times better cooling performance than traditional heat sinks.
Pricing and Market Impact
While exact prices for these next-gen cooling technologies are not yet available, initial estimates suggest they will be competitively priced with high-end active cooling solutions. Their impact, however, could be enormous. By offering efficient, silent, and reliable cooling, they could redefine the standards for electronic device design and performance.
Conclusion
As we continue to push the boundaries of electronics, cooling will play an increasingly crucial role. And while it may not command the spotlight like a flashy new processor or a stunning OLED display, the silent ascendancy of next-gen passive cooling tech is a revolution in its own right—one that promises to usher in a new era of quieter, more efficient, and more reliable electronics.